Mold illness statistics in the United States reveal that almost half of residential buildings are affected by mold.
The prevalence and cost of mold-related illnesses in the United States are a cause for concern, with almost half of residential buildings affected by mold. This has significant economic implications, as the average cost of mold remediation ranges from $1,373 to $3,325. The impact of mold-related infections is profound, contributing to an annual economic burden of $5.6 billion, while asthma cases linked to dampness and mold add an additional $16.8 billion to the overall cost. These staggering figures shed light on the substantial financial toll of mold-related health issues in the country, emphasizing the need for effective preventive measures and timely intervention.
Furthermore, the prevalence of mold-related illnesses raises questions about the common symptoms and health risks associated with mold exposure. It is essential to understand the implications of these statistics on public health and the broader real estate market. By delving deeper into the common symptoms and health risks, individuals and policymakers can gain a comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted impact of mold-related illnesses, leading to more informed decision-making and proactive measures to address this pressing public health issue.
Understanding the Prevalence and Cost of Mold-Related Illnesses in the United States
Mold-related illnesses have become a significant concern in the United States, affecting nearly 47% of residential buildings and resulting in a substantial economic burden for remediation efforts. The average cost of mold remediation ranges from $1,373 to $3,325, with an average expense of $2,347, highlighting the financial impact of addressing mold issues. These statistics underscore the widespread nature of mold in residential buildings and the associated costs, which can have implications for homeowners, real estate markets, and public health.
Furthermore, the economic impact of mold-related infections and asthma cases linked to mold exposure in the US is estimated at $5.6 billion annually, with an additional $16.8 billion attributed to asthma cases associated with dampness and mold. These figures emphasize the significant public health implications and the considerable financial burden imposed by mold-related illnesses. The high prevalence of mold in residential buildings and its connection to respiratory conditions like asthma underscores the urgent need for effective preventive measures and interventions to mitigate the health risks posed by mold exposure. These statistics prompt a deeper understanding of the broader impact of mold-related illnesses on public health and the economy, necessitating proactive strategies to address this pervasive issue.
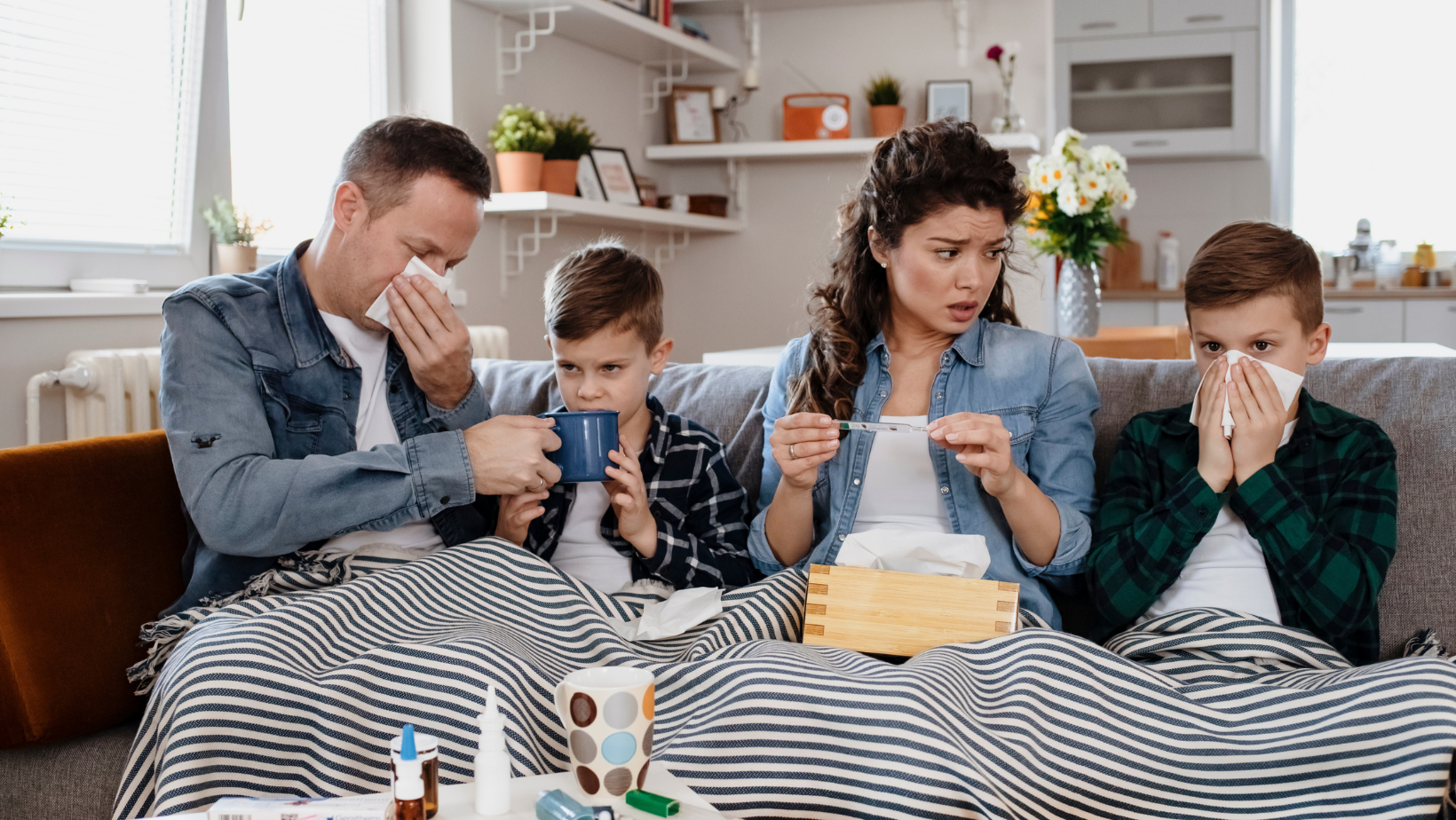

Health Risks and Common Symptoms of Mold Illness
Mold exposure poses significant health risks and can lead to various adverse effects on individuals. Respiratory problems, such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, are common symptoms associated with mold illness. In addition, allergic reactions, such as skin rashes, itchy eyes, and nasal congestion, can also be triggered by exposure to mold spores. These symptoms highlight the potential dangers of mold exposure and emphasize the importance of addressing this issue.
Furthermore, mold has been linked to a clear association with asthma symptoms, particularly in damp or mold-infested environments. Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to breathing difficulties. The presence of mold in indoor spaces can exacerbate asthma symptoms and contribute to the worsening of respiratory health in affected individuals. This underscores the critical impact of mold on respiratory health and the need for effective preventive measures to mitigate these risks.
Moreover, the long-term health implications of mold exposure cannot be overlooked. Prolonged exposure to mold has been associated with chronic respiratory conditions, persistent allergic reactions, and potential immune system disruptions. These long-term health implications highlight the importance of raising awareness about mold-related illnesses and implementing proactive measures to prevent and address mold growth in residential and commercial environments. By understanding the common symptoms and health risks associated with mold illness, individuals can take informed steps to protect their well-being and minimize the impact of mold on their health.

Impact on Residential and Commercial Buildings
The impact of mold on residential and commercial buildings in the United States goes beyond the physical presence of the fungus. Mold not only affects the structural integrity of buildings but also has far-reaching implications for the real estate market. For instance, the discovery of mold in residential properties often results in a significant decrease in home resale values, ranging from 20-37%. This substantial decline underscores the financial ramifications of mold infestation, affecting both homeowners and the broader real estate industry. The economic consequences of mold-related issues in residential buildings necessitate efficient preventive measures and timely remediation to mitigate financial losses and maintain property values.
Moreover, the challenges posed by mold are not limited to residential properties. Schools and commercial office buildings are also vulnerable to mold growth, primarily due to underlying plumbing and roofing problems. According to statistics, approximately 30% of schools in the US experience plumbing issues [1], while 27% encounter roofing problems that could potentially lead to the development of mold [1]. These conditions not only compromise the structural integrity of the buildings but also pose health risks to students, teachers, employees, and visitors. As a result, the presence of mold in educational institutions and commercial office spaces may necessitate costly remediation efforts to ensure the health and well-being of occupants, emphasizing the urgency of addressing mold-related issues in non-residential buildings [1].
These examples illustrate the pervasive impact of mold on both residential and commercial buildings, emphasizing the need for comprehensive preventive measures and prompt remediation efforts to safeguard property values and the health of occupants.
[1] Source: https://www.rubyhome.com/blog/mold-stats Source: https://realtimelab.com/mold-statistics
Preventive Measures, Remediation, and Treatment Options
Preventive measures play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of mold growth in residential and commercial buildings. By addressing the root causes of mold, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of mold-related illnesses and the associated economic burden. For instance, fixing leaks in plumbing systems, roofs, and windows is essential to prevent water intrusion, which can create the ideal environment for mold to thrive. Additionally, reducing indoor humidity levels through the use of dehumidifiers and ensuring proper ventilation in damp areas such as basements and attics can effectively deter mold growth.
Furthermore, the utilization of mold-resistant products, such as paints and building materials, can offer long-term protection against mold infestations. These products are designed to inhibit the growth of mold and mildew, providing an additional layer of defense for residential and commercial properties. Moreover, maintaining cleanliness through regular housekeeping practices, including dusting, vacuuming, and cleaning with mold-inhibiting solutions, can help prevent the accumulation of mold spores and minimize the risk of exposure.
In the event of mold contamination, professional mold remediation becomes necessary to address the issue effectively. The costs associated with mold remediation can vary based on the extent of the infestation, the size of the affected area, and the specific methods employed for removal. For instance, mold remediation costs may range from minor interventions, such as localized cleaning and sanitization, to more extensive procedures involving the removal and replacement of mold-affected materials. The financial implications of mold remediation underscore the importance of implementing preventive measures to minimize the likelihood of mold proliferation and the need for costly remediation efforts.
Furthermore, treatment options for mold-related illnesses should be approached with a focus on preventive strategies and timely intervention. Individuals experiencing symptoms of mold illness, such as respiratory issues or allergic reactions, should seek medical attention to address their condition. Treatment may involve alleviating symptoms through medication and supportive care, as well as implementing measures to reduce ongoing mold exposure in the affected environment. By integrating treatment options with preventive measures, individuals can mitigate the health risks associated with mold-related illnesses and contribute to a healthier living and working environment [1].

Global Impact of Mold-Related Health Issues
The impact of mold-related health issues extends beyond the United States, affecting populations worldwide. Indoor contaminants, including mold, have been found to contribute significantly to serious health problems and economic costs on a global scale. For example, in India, outdoor and indoor air pollution is a serious environmental risk factor, leading to 104 deaths per day and 38,000 deaths per year in one region alone. This highlights the profound impact of mold and other indoor pollutants on public health, emphasizing the urgent need for international attention and preventive measures.
Furthermore, statistics reveal that 92% of the world's population lives in places where air quality levels exceed the limits set by the World Health Organization. This widespread exposure to poor air quality, often exacerbated by mold and indoor contaminants, underscores the significance of addressing this issue on a global level. The economic burden of mold-related health problems is also substantial, with indoor air pollution estimated to be responsible for the annual loss of over 200,000 healthy life years in the U.K. [3].
These statistics serve as compelling evidence of the far-reaching consequences of mold-related illnesses and the urgent need for coordinated efforts to promote public health and environmental well-being.
Click for more information on Mastertech Environmental or Mastertech Franchise Systems.